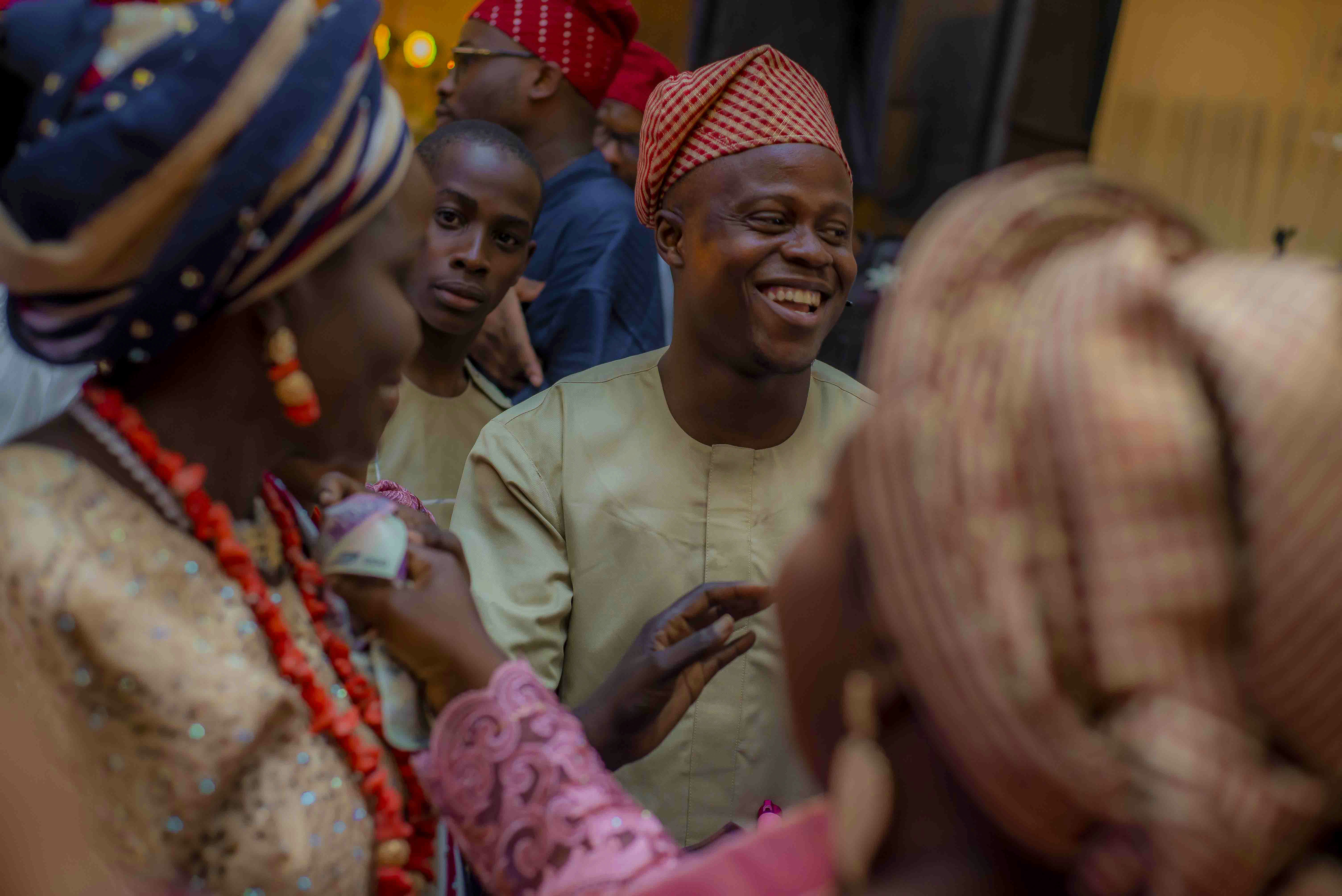
Understanding Cultural Adaptation in Ghana
Cultural adaptation refers to the process through which individuals and communities adjust to new cultural contexts while maintaining their unique identity. In the case of Ghana, as globalization influences various aspects of life, the necessity for cultural adaptation becomes increasingly significant. Ghana is characterized by a rich and diverse cultural heritage, encompassing an array of languages, traditions, and values that play a critical role in how its people respond to global changes.
One of the essential elements of cultural adaptation in Ghana is language. With over 80 languages spoken throughout the country, including Akan, Ewe, and Hausa, effective communication becomes vital as Ghanaian communities engage with broader global narratives. The intertwining of indigenous languages with foreign tongues, particularly English, represents an ongoing negotiation of identity and adaptability. This linguistic interplay enables Ghanaians to express their cultural roots while also assimilating aspects of global communication.
Furthermore, traditional practices and values hold immense significance in Ghanaian society. The adherence to cultural norms surrounding family structure, social interactions, and communal responsibilities often guides individuals as they navigate the complexities presented by globalization. Ghanaian values, deeply rooted in respect, hospitality, and community welfare, serve as a foundation upon which adaptation strategies can be built. These values foster resilience, allowing individuals to embrace global influences while remaining grounded in local customs.
In essence, understanding cultural adaptation in Ghana is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses language, traditions, and values. As Ghanaians interact with the wider world, the blending of these components facilitates a harmonious balance between preserving cultural integrity and engaging with global citizenship. The richness of Ghanaian culture not only informs adaptation strategies but also highlights the importance of cultural identity in a rapidly changing environment.
Historical Influences on Ghanaian Culture
Ghanaian culture is intricately woven into the rich tapestry of its historical evolution, shaped by diverse factors that include colonialism, the quest for independence, and cross-cultural interactions. From early civilizations, such as the Akan and Mole-Dagbani groups, Ghana has been a melting pot of ethnic identities, traditions, and customs. These historical roots have laid a solid foundation for contemporary Ghanaian cultural expressions and adaptation strategies in a globalized world.
The impact of colonialism, which commenced in the late 15th century with the arrival of European traders, played a significant role in altering the trajectory of Ghanaian culture. British colonial rule fundamentally transformed societal structures, economies, and cultural practices. The imposition of Western education and religious ideologies led to a reexamination of traditional beliefs and practices. Nevertheless, Ghanaians sought to retain their indigenous customs while adapting to the imposed systems, leading to a synthesis of cultural practices that still exists today.
Following independence in 1957, Ghana asserted its cultural identity amid global influences, seeking to celebrate and revitalize traditional customs while navigating the complexities of modernity. This period marked a resurgence in traditional art, music, and festivals as symbols of national pride. Ghanaians have continually embraced their historical significance, fostering a sense of unity amid cultural diversity. Additionally, interactions with other cultures, spurred by globalization, have further enriched Ghanaian practices, enabling the emergence of hybrid cultural expressions.
As contemporary Ghana navigates an interconnected world, the significance of traditional practices remains steadfast. They serve not only as links to the past but also as vital components in the strategies employed for cultural adaptation. By understanding their historical influences, Ghanaians are better equipped to embrace globalization while ensuring their rich cultural heritage remains intact.
Modernization and Globalization Effects on Ghanaian Culture
The interplay between modernization and globalization has significantly impacted Ghanaian culture, leading to an evolving landscape where traditional practices coexist with contemporary influences. Globalization facilitates the exchange of ideas, customs, and technologies across borders, creating diverse opportunities for cultural expression. However, this increasing interconnectivity also poses challenges to the preservation of Ghana’s rich cultural heritage.
One notable effect of globalization is the accessibility of information and communication technologies. These tools allow for the widespread dissemination of cultural content, enabling Ghanaians to engage with global trends and practices. Consequently, younger generations are increasingly exposed to foreign lifestyles, which may lead to the adoption of contemporary customs at the expense of traditional practices. This modernization poses a challenge, as the essence of Ghanaian identity can be overshadowed by external influences, often leading to a dilution of cultural values and norms.
On the other hand, globalization provides Ghanaian culture with unique opportunities for revitalization. The global stage allows for the celebration of Ghanaian cultural practices, such as traditional music, dance, and art, attracting international attention and appreciation. Moreover, Ghanaians have the ability to reinterpret their cultural expressions through modern forms, such as fusion genres in music that blend traditional and contemporary styles. This adaptability fosters cultural resilience, as it encourages the community to embrace their heritage while innovating to remain relevant in a fast-paced world.
Ultimately, the challenge lies in finding a delicate balance between honoring traditional values and embracing the advancements of modernization. The ongoing dialogue within Ghanaian communities is crucial to encourage a culture that acknowledges its past while confidently engaging with the future. This balance offers a unique standpoint for Ghana to navigate the influences of globalization while safeguarding its cultural identity for generations to come.
Key Strategies for Cultural Adaptation in Ghana
In a rapidly globalizing world, Ghanaians have developed various strategies to adapt culturally while maintaining their unique identities. These strategies encompass education, cultural festivals, community engagement, and media, all of which play significant roles in reinforcing cultural ties alongside the adoption of global influences.
Education serves as a cornerstone for cultural adaptation in Ghana. Institutions, both formal and informal, are pivotal in imparting traditional values and practices to younger generations. Many schools incorporate local history, languages, and customs into their curriculum, allowing students to appreciate their heritage while also preparing them for participation in the global community. Programs such as the Ghana National Commission for UNESCO’s initiatives promote cultural education and awareness, fostering a proud identity rooted in local traditions.
Cultural festivals across different regions further exemplify the vibrancy of Ghanaian traditions. Events such as the Homowo Festival in Accra and the Panafest in Cape Coast not only celebrate Ghanaian culture but also serve as platforms for showcasing the richness of local artistry and heritage to a broader audience. These festivals draw both local and international tourists, thereby creating opportunities for cultural exchange and economic development while simultaneously reinforcing community bonds and cultural pride.
Community engagement is another essential strategy for cultural adaptation in Ghana. Local organizations and grassroots movements actively promote initiatives that encourage the sharing and preservation of cultural practices. For instance, community groups often collaborate on projects that aim to revitalize traditional crafts, music, and dance, fostering a sense of belonging and continuity among members while embracing modern influences.
Lastly, media plays a transformative role in shaping cultural narratives in Ghana. With the rise of digital platforms, Ghanaians are increasingly able to share their stories, music, and art with a global audience. This not only facilitates cultural exchange but also helps reinforce cultural identity among Ghanaians living abroad, making them feel connected to their roots despite geographical distances.
The Role of Technology in Cultural Adaptation
Technology serves as a powerful catalyst in facilitating cultural adaptation processes, particularly in a rapidly globalizing world. In Ghana, the influence of technological advancements is evident in various dimensions of cultural expression and community engagement. Social media platforms, digital applications, and mobile communication have transformed how Ghanaians preserve, adapt, and share their cultural heritage. With increasing access to the internet, more individuals engage with their cultural practices through online platforms, leading to enhanced visibility and interaction.
Social media has become an essential tool for Ghanaians to showcase cultural events, traditional attire, and culinary practices to a broader audience. This digital landscape allows for a combination of local and global influences, creating a dynamic cultural exchange. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter enable users to celebrate cultural festivities, such as the Akwasidae and Homowo, by posting pictures, videos, and live performances. As a result, such events gain international recognition, encouraging the appreciation of Ghanaian culture globally.
Moreover, mobile communication technologies have contributed significantly to the dissemination of cultural narratives. Text messaging, instant messaging apps, and online forums provide spaces for discussions about identity, heritage, and modern Ghanaian life. This interactivity fosters a sense of belonging and nostalgia among Ghanaians, both at home and in the diaspora, as they connect with peers who share similar cultural experiences.
Additionally, digital platforms host cultural content that educates users about traditional practices, languages, and histories, helping younger generations maintain a connection to their roots. As educational resources expand online, Ghanaians can access materials that promote cultural learning and appreciation, thereby reinforcing their identity in the context of globalization. Thus, technology plays a pivotal role in the ongoing evolution and adaptation of Ghanaian culture, enabling both preservation and transformation within a globalized framework.
Intergenerational Perspectives on Cultural Adaptation
The process of cultural adaptation in Ghana offers rich insights when viewed through the lens of intergenerational perspectives. Younger Ghanaians are increasingly faced with the challenge of balancing traditional values with the influences of globalization. This balancing act necessitates an understanding of their cultural roots while also navigating new social norms and technologies that permeate contemporary life.
Younger generations, often labeled as digital natives, are integrating modern practices into their day-to-day existence. This integration is not merely a rejection of tradition, but rather a reimagining of what it means to be Ghanaian in a global context. For instance, social media platforms have become a significant avenue for expressing and sharing cultural experiences, allowing young people to engage with their heritage while simultaneously adopting global trends.
Conversely, the role of elders in this cultural adaptation journey cannot be overlooked. Older generations hold a wealth of knowledge about traditional practices, values, and beliefs. They are tasked with the responsibility of ensuring that these cultural tenets are preserved and passed on to the youth. This transfer of knowledge often occurs through storytelling, communal events, and mentorship. Elders serve as touchpoints for the youth, providing guidance and insight into the importance of cultural identity in an increasingly interconnected world.
However, the dynamics between the generations can sometimes lead to tension. Younger Ghanaians may perceive traditional practices as outdated or irrelevant, while older individuals may view contemporary influences as eroding the essence of Ghanaian culture. Bridging this gap requires open dialogues that foster mutual respect and understanding, ensuring that cultural adaptation is a collaborative effort. In this manner, both generations can contribute to evolving cultural practices that honor the past while embracing the future.
Challenges to Cultural Adaptation in Ghana
In the context of globalization, Ghanaians encounter various challenges as they strive to adapt their rich cultural heritage to the evolving global landscape. One significant issue is cultural erosion, which occurs when traditional values, practices, and expressions become diluted or replaced by foreign influences. This phenomenon is particularly evident among the younger generation, who may prioritize modern lifestyles and global trends over their ancestral customs. The result is a gradual loss of unique cultural identifiers that have historically contributed to a cohesive societal structure.
Another challenge is the identity crisis faced by many Ghanaians. As individuals grapple with the duality of local and global identities, they may feel disconnected from their cultural roots, leading to feelings of alienation. This state of confusion is exacerbated by the influx of information and cultural practices facilitated by technology and social media, which create a complex interplay between devotion to traditional customs and the pursuit of a global identity. Consequently, Ghanaians may find themselves struggling to integrate these competing identities, leading to increased anxiety and uncertainty about their place in society.
Socio-economic factors also pose considerable challenges to cultural adaptation. Rapid urbanization has led to significant demographic shifts, with many individuals migrating from rural to urban areas in search of better opportunities. This transition often results in a detachment from communal living and traditional practices. Urban environments, characterized by their diverse populations and fast-paced lifestyles, may inadvertently pressure Ghanaians to conform to more homogenized cultural expressions. Furthermore, the commercialization of culture can lead to a superficial understanding of cultural elements, reducing their significance and relevance within local contexts.
In summary, the interplay of cultural erosion, identity crises, and socio-economic factors presents considerable obstacles for Ghanaians navigating cultural adaptation in a globalized world. Addressing these issues is crucial for preserving the rich cultural heritage that defines Ghanaian identity.
Success Stories of Cultural Adaptation
In recent years, several individuals and communities in Ghana have exemplified successful cultural adaptation strategies that demonstrate resilience while embracing the dynamics of globalization. One notable case is the “Fante Cultural Festival” held annually in the Central Region. This festival not only celebrates the unique cultural heritage of the Fante people but also incorporates contemporary elements, drawing both local and international tourists. Through music, art, and culinary showcases, the festival serves as a platform for cultural exchange, fostering a sense of pride among participants while promoting cultural education.
Another compelling example can be found in the creative arts sector, where numerous Ghanaian artists and musicians have harnessed global influences to cultivate unique expressions that resonate with both local and international audiences. Artists such as Sarkodie and Stonebwoy have successfully blended traditional Ghanaian music styles, such as hiplife and reggae, with international genres like hip-hop and dancehall. Their work not only preserves cultural elements but also appeals to a broader audience, illustrating the potential for cultural adaptation to drive artistic innovation.
Furthermore, initiatives like “Adinkra Market,” a cooperative of artisans in Accra, showcase how traditional craftsmanship can adapt to modern consumer demands. Artisans collaborate to create contemporary products that retain traditional designs while appealing to the tastes of a global market. This approach not only supports local economies but also sustains the cultural heritage represented in Adinkra symbols.
These success stories underline the potential for cultural adaptation strategies to thrive in an era of globalization. By embracing innovation while honoring traditional customs, communities in Ghana are not just surviving but thriving, demonstrating that cultural resilience can coexist with change. Such initiatives have effectively illustrated how cultural adaptation can empower individuals and communities, ensuring that Ghana’s rich heritage continues to flourish in a global context.
Future Trends in Ghanaian Cultural Adaptation
The landscape of Ghanaian culture is continually transforming in response to an array of global influences and challenges. As globalization accelerates, future trends in Ghanaian cultural adaptation will likely reflect an increasing hybridization of local traditions and global practices. This amalgamation is driven by the diaspora, digital communication, and economic interdependence, which facilitate sustained cultural exchanges between Ghana and the wider world.
One prominent trend expected in the near future is the increased visibility and representation of Ghanaian culture on international platforms. With the expansion of digital media, Ghanaian artists, musicians, and creators can reach global audiences, garnering interest in their unique cultural expressions. As a result, this exposure can lead to a resurgence of interest in traditional practices, customs, and art forms, showcasing their relevance in contemporary society. This interaction not only revitalizes local culture but also fosters a sense of pride among Ghanaians, paving the way for cultural evolution that honors its roots while embracing modernity.
Additionally, the impact of global challenges, such as climate change and ongoing technological advancements, will necessitate new adaptation strategies within Ghanaian society. Local communities may increasingly incorporate sustainable practices informed by both traditional knowledge and modern innovations. For instance, traditional agricultural methods might evolve through the integration of technology, improving resilience against environmental threats while preserving indigenous techniques.
As Ghana navigates this complex landscape, the potential for cultural exchange is immense. Increasing interconnectedness may encourage collaborative efforts between local and international communities, sparking dialogues around cultural identity, heritage preservation, and contemporary issues. As Ghana continues to evolve amidst a changing global context, the journey toward cultural adaptation promises to be both dynamic and multifaceted.